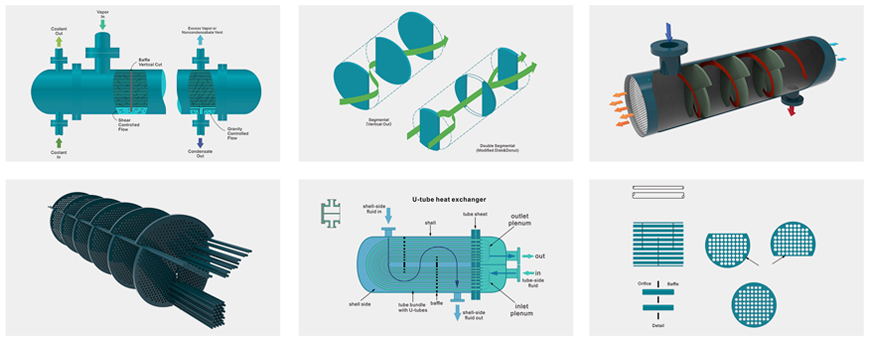
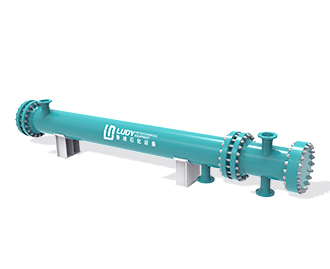
Shell-and-tube heat exchanger is widely used in upstream and downstream equipment for efficient heat transfer from one medium to another. The heat exchanger is divided into parallel flow and counter flow according to the flow arrangement. Parallel flow and counter flow. Parallel flow (common flow) is the flow generated when two fluids enter the exchanger at the same end and flow to the other end in parallel. Counter flow refers to two kinds of fluid from opposite ends into the exchanger.
The purpose of the heat exchanger may vary depending on the process requirements, such as hot and cold liquid, heat recovery, separation, reboiler, condensation.
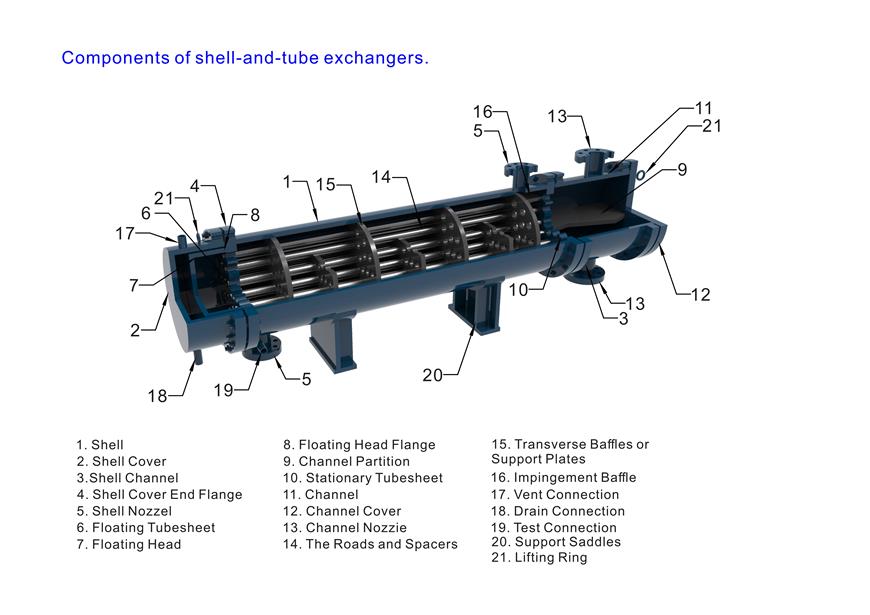
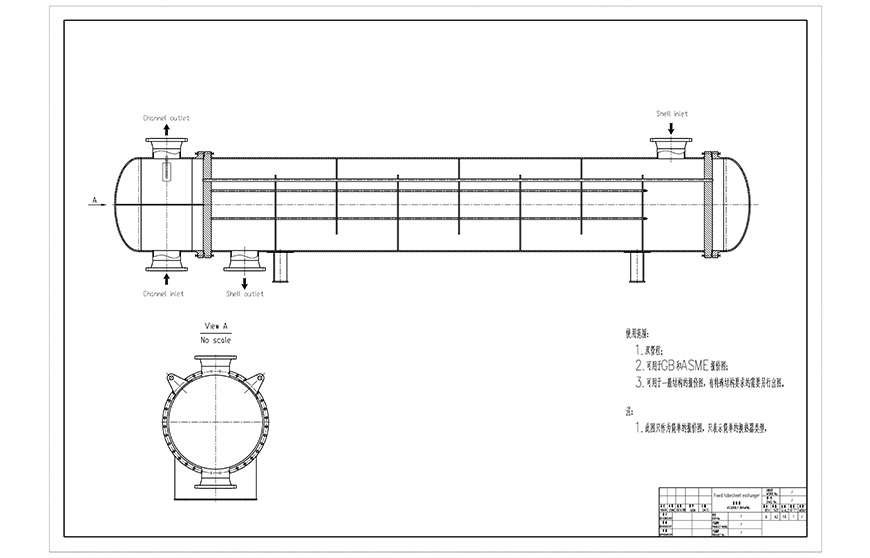
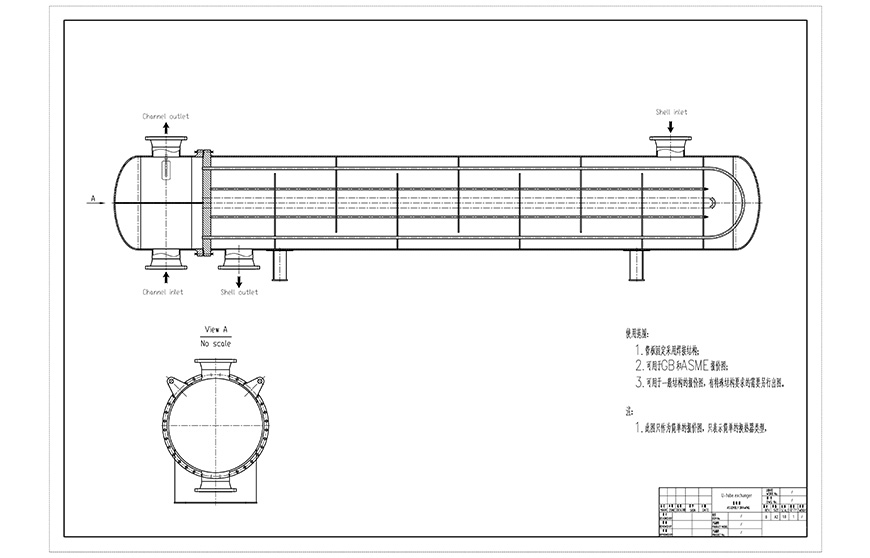
The basic types of shell and tube heat exchanger are: fixed tube sheet, floating head and U-tube.

Shell-and-tube heat exchanger is composed of shell, heat transfer tube bundle, tube sheet, baffle and tube box. The fluid channel formed in the heat exchange tube is called the tube side, and the fluid channel formed outside the heat exchange tube is called the shell side. When the tube side and shell side pass through two different temperature fluids, the higher temperature fluid transfers heat to the lower temperature fluid through the heat exchange tube wall. The higher temperature fluid is cooled and the lower temperature fluid is heated, thus realizing the purpose of two fluid heat exchange process.
The configuration of shell and tube heat exchanger depends on the requirements of each process. Major design considerations should include fluid, corrosion potential, cleaning issues, pressure drop, heat transfer efficiency, and piping (typically 20 feet and 20 feet).

Shell-and-tube heat exchanger is used as a part of well testing device, which is mainly used in well testing and well flushing.